NOTE: This article was updated with an addendum and additional data.
Inspired by Michael Benedict's original blog post on monitoring SMS delivery reliability in Tanzania and recent reports of SMS keyword blocking in Uganda, MobileActive.org set out to replicate Michael's work - and add to it. SMS is such a crucial part of many mobile projects and just day-to-day life across the developing world, yet there’s a lack of public knowledge of mobile network operator interdependency, latency, and reliability (how mobile network operators work together to transmit SMS, the lag time between sending and receiving a message, and the guarantee that a message will reach its recipient).
Michael's post got us thinking: Can this type of experiment be replicated without extra hardware required (GPRS modems, etc.)? After a few quick brainstorming sessions at the OpenMobile Lab in New York, we created an alpha version of a mobile application that recreates a number of latency tests. It’s far from perfect - and there is still plenty of work to be done - but we’re confident that this project will lead us to extremely valuable data about the transparency and reliability of SMS on mobile networks.
SMSTester - The App
SMSTester is a simple Android app that allows a user create a set of keywords to be sent as SMS messages. This allows the user to explore differences in latency for any type of message - from basic, everyday text like ‘milk’ or ‘newspaper’ to politically inflammatory text such as ‘revolution.’ We then set up a logging mechanism to timestamp and record each SMS as it is sent (from the sender side) or received (on the receipt side). By comparing the sent and received timestamps, we’re very easily able to calculate message latency from one SIM to another.
Initial Deployment
We deployed SMSTester in a test in Egypt a few weeks ago. As this was the initial trial for a fully untested application, we were careful. While we did run our tests across a number of local mobile operator networks, we kept the test volume small enough to keep us under the radar (for now!). Our test methodology included:
- Testing across all three major mobile operator networks in Egypt: Etisalat, Mobinil, and Vodafone
- Consistent keyword test bed containing both ‘safe’ and ‘political’ terms, where ‘safe’ refers to everyday vocabulary and ‘political’ refers to politically sensitive words
- Language coverage across both English and Arabic
- Roughly 270 messages successfully sent, received and analyzed
What We Looked For And Why
The main focus of our analysis was SMS delivery latency, delay, or more generally, delivery failures. There are plenty of anecdotal stories of seemingly random delays lasting multiple hours or even days in many countries where we work. While network congestion and growing infrastructure are often to blame for SMS unreliability, there are also legitimate concern that delays may be an indication of deliberate message filtering and monitoring. What has emerged is an environment in which activists and human rights defenders are unable to clearly understand what networks - and what behavior - is safe or hazardous for themselves or their contacts. The end goal of this research, put simply, is to change this paradigm. Rumors of keyword filtering are not helpful; what is helpful is any evidence of surveillance.
This small experiment is just a start, of course. Our hypothesis is that keyword filtering and other malicious behavior on the part of mobile network operators may manifest in the form of increased message latency or overt message blockage. If we could detect any sign of a correlation between message content and delivery with just some initial testing in-country, this would be a great first step towards our overall goal. However it’s very important to note that while message latency or failure may be indicative of bad behavior on the part of the carries, it could be due to any number of contributing factors and is by no means an implication of foul play. For now we’re merely hypothesizing.
Results
Despite the minor bugs discovered, we gathered very valuable information about message latency in Egypt during this trial. The most valuable data was on the Etisalat network (also known as the Emirates Telecommunications Corporation), based in the UAE. The majority of the data we recovered from this trial was between an Etisalat SIM and other Egyptian networks. (Note: This was the result of inadvertent data loss for other test scenarios and we did not specifically target Etisalat).
Main Conclusions
Big Caveat (READ THIS!): Given the small sample size of this test, it should be noted that none of these conclusions are definitive. In fact, the very nature of such a small sample size warrants much further investigation.
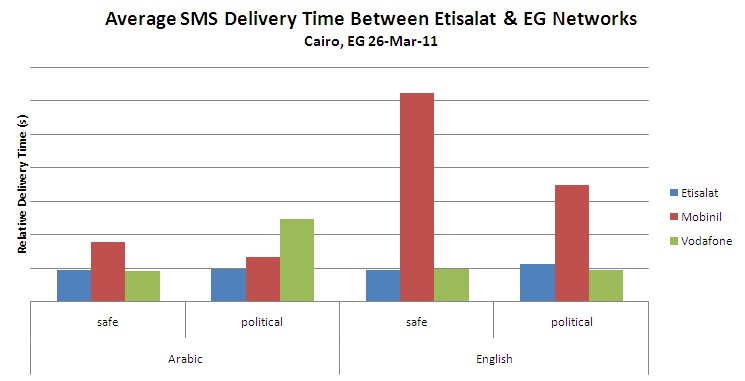
(1) Delivery between Etisalat & Mobinil networks warrants further investigation. As shown below, the delivery time for English language text messages from Etisalat to Mobinil is significantly greater than delivery time to any other network, for both English and Arabic texts. This may be due to any number of network delays, and it may also be indicative of English language filtering by one or both of the mobile network operators.
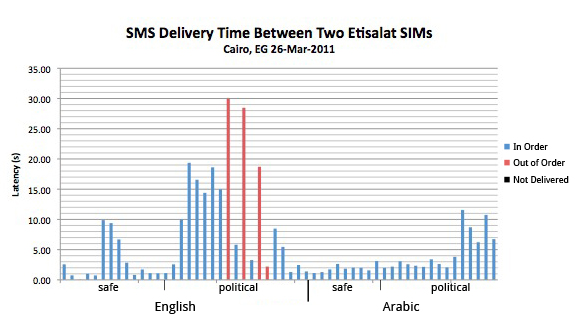
(2) Delivery time of politically sensitive English messages on Etisalat warrants further investigation. The chart below shows that politically sensitive English messages sent across the Etisalat network were delivered with significantly more latency than others, with the possible exception of politically sensitive Arabic messages. In addition, each of the three messages that were delivered out of order fell into this category. Similar to the above conclusion, this may be indicative of specific filtering on behalf of Etisalat.